Sued by Meta, Freenom Halts Domain Registrations
The domain name registrar Freenom, whose free domain names have long been a draw for spammers and phishers, has stopped allowing new domain name registrations. The move comes just days after the Dutch registrar was sued by Meta, which alleges the company ignores abuse complaints about phishing websites while monetizing traffic to those abusive domains.
The domain name registrar Freenom, whose free domain names have long been a draw for spammers and phishers, has stopped allowing new domain name registrations. The move comes after the Dutch registrar was sued by Meta, which alleges the company ignores abuse complaints about phishing websites while monetizing traffic to those abusive domains.
Freenom is the domain name registry service provider for five so-called “country code top level domains” (ccTLDs), including .cf for the Central African Republic; .ga for Gabon; .gq for Equatorial Guinea; .ml for Mali; and .tk for Tokelau.
Freenom has always waived the registration fees for domains in these country-code domains, presumably as a way to encourage users to pay for related services, such as registering a .com or .net domain, for which Freenom does charge a fee.
On March 3, 2023, social media giant Meta sued Freenom in a Northern California court, alleging cybersquatting violations and trademark infringement. The lawsuit also seeks information about the identities of 20 different “John Does” — Freenom customers that Meta says have been particularly active in phishing attacks against Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp users.
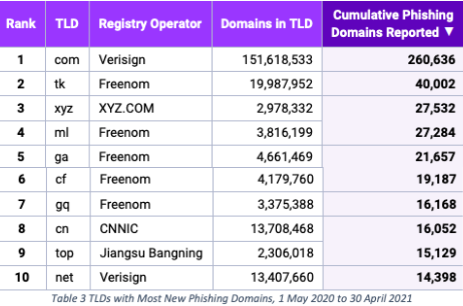
The lawsuit points to a 2021 study (PDF) on the abuse of domains conducted by Interisle Consulting Group, which discovered that those ccTLDs operated by Freenom made up five of the Top Ten TLDs most abused by phishers.
“The five ccTLDs to which Freenom provides its services are the TLDs of choice for cybercriminals because Freenom provides free domain name registration services and shields its customers’ identity, even after being presented with evidence that the domain names are being used for illegal purposes,” the complaint charges. “Even after receiving notices of infringement or phishing by its customers, Freenom continues to license new infringing domain names to those same customers.”
Meta further alleges that “Freenom has repeatedly failed to take appropriate steps to investigate and respond appropriately to reports of abuse,” and that it monetizes the traffic from infringing domains by reselling them and by adding “parking pages” that redirect visitors to other commercial websites, websites with pornographic content, and websites used for malicious activity like phishing.
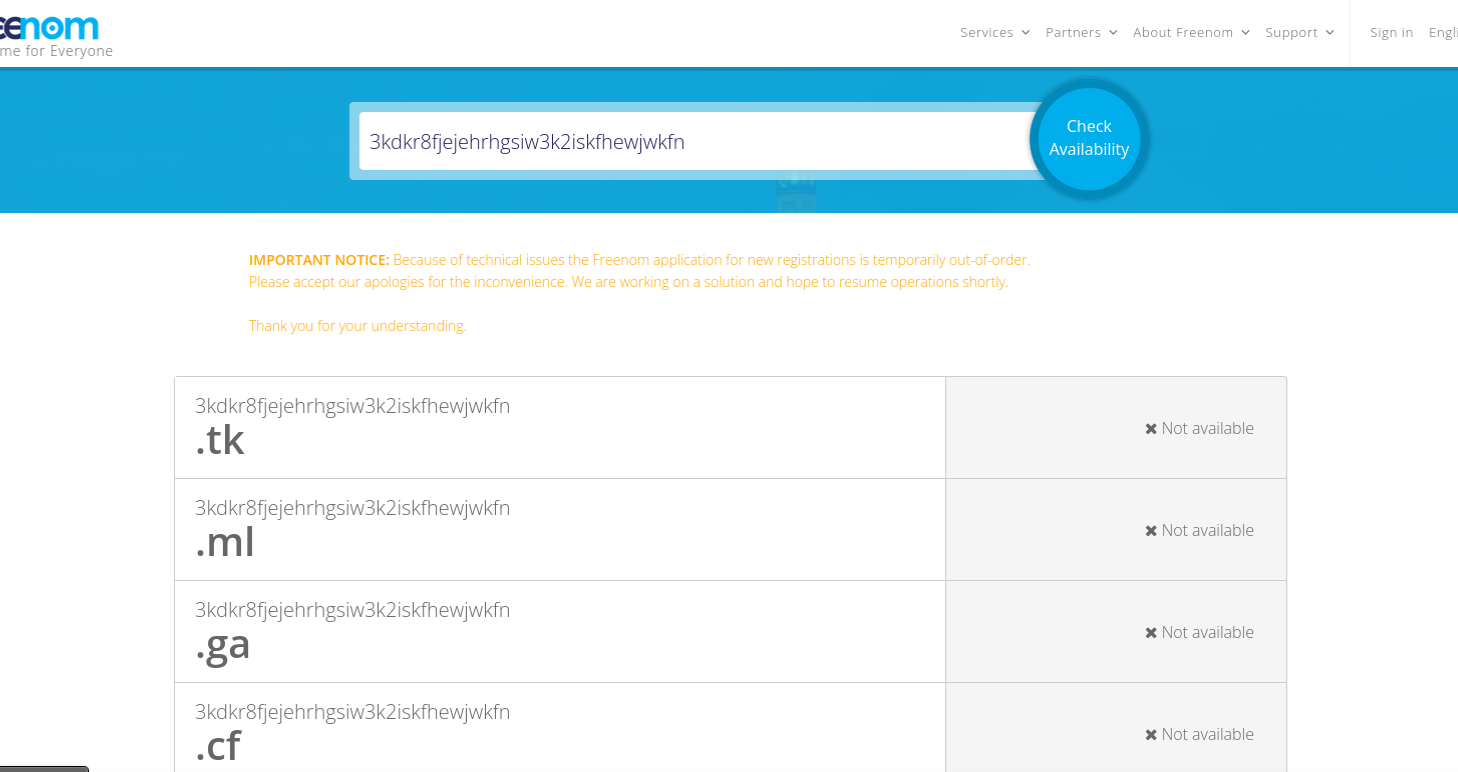
Freenom has not yet responded to requests for comment. But attempts to register a domain through the company’s website as of publication time generated an error message that reads:
“Because of technical issues the Freenom application for new registrations is temporarily out-of-order. Please accept our apologies for the inconvenience. We are working on a solution and hope to resume operations shortly. Thank you for your understanding.”

Image: Interisle Consulting Group, Phishing Landscape 2021, Sept. 2021.
Although Freenom is based in The Netherlands, some of its other sister companies named as defendants in the lawsuit are incorporated in the United States.
Meta initially filed this lawsuit in December 2022, but it asked the court to seal the case, which would have restricted public access to court documents in the dispute. That request was denied, and Meta amended and re-filed the lawsuit last week.
According to Meta, this isn’t just a case of another domain name registrar ignoring abuse complaints because it’s bad for business. The lawsuit alleges that the owners of Freenom “are part of a web of companies created to facilitate cybersquatting, all for the benefit of Freenom.”
“On information and belief, one or more of the ccTLD Service Providers, ID Shield, Yoursafe, Freedom Registry, Fintag, Cervesia, VTL, Joost Zuurbier Management Services B.V., and Doe Defendants were created to hide assets, ensure unlawful activity including cybersquatting and phishing goes undetected, and to further the goals of Freenom,” Meta charged.
It remains unclear why Freenom has stopped allowing domain registration. In June 2015, ICANN suspended Freenom’s ability to create new domain names or initiate inbound transfers of domain names for 90 days. According to Meta, the suspension was premised on ICANN’s determination that Freenom “has engaged in a pattern and practice of trafficking in or use of domain names identical or confusingly similar to a trademark or service mark of a third party in which the Registered Name Holder has no rights or legitimate interest.”
A spokesperson for ICANN said the organization has no insight as to why Freenom might have stopped registering domain names. But it said Freenom (d/b/a OpenTLD B.V.) also received formal enforcement notices from ICANN in 2017 and 2020 for violating different obligations.
A copy of the amended complaint against Freenom, et. al, is available here (PDF).
March 8, 6:11 p.m. ET: Updated story with response from ICANN. Corrected attribution of the domain abuse report.