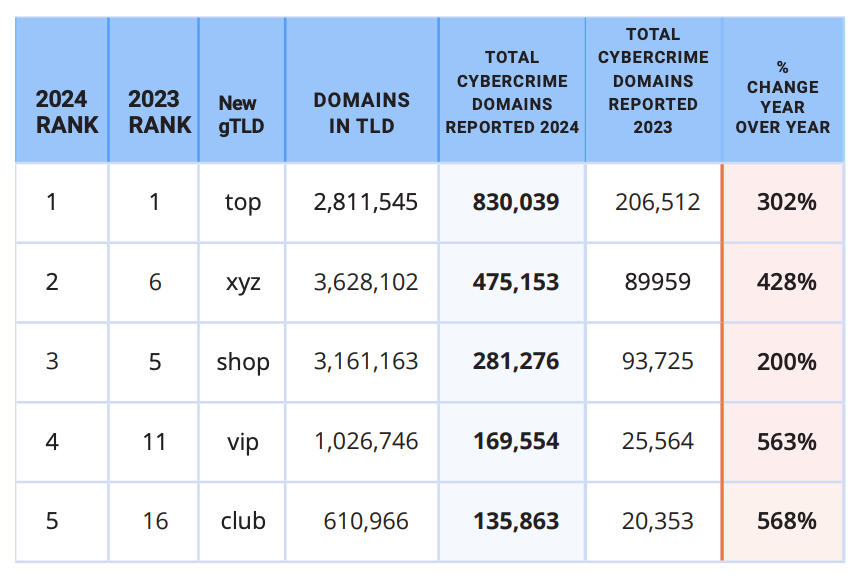
Many Public Salesforce Sites are Leaking Private Data
A shocking number of organizations -- including banks and healthcare providers -- are leaking private and sensitive information from their public Salesforce Community websites, KrebsOnSecurity has learned. The data exposures all stem from a misconfiguration in Salesforce Community that allows an unauthenticated user to access records that should only be available after logging in.
A shocking number of organizations — including banks and healthcare providers — are leaking private and sensitive information from their public Salesforce Community websites, KrebsOnSecurity has learned. The data exposures all stem from a misconfiguration in Salesforce Community that allows an unauthenticated user to access records that should only be available after logging in.
A researcher found DC Health had five Salesforce Community sites exposing data.
Salesforce Community is a widely-used cloud-based software product that makes it easy for organizations to quickly create websites. Customers can access a Salesforce Community website in two ways: Authenticated access (requiring login), and guest user access (no login required). The guest access feature allows unauthenticated users to view specific content and resources without needing to log in.
However, sometimes Salesforce administrators mistakenly grant guest users access to internal resources, which can cause unauthorized users to access an organization’s private information and lead to potential data leaks.
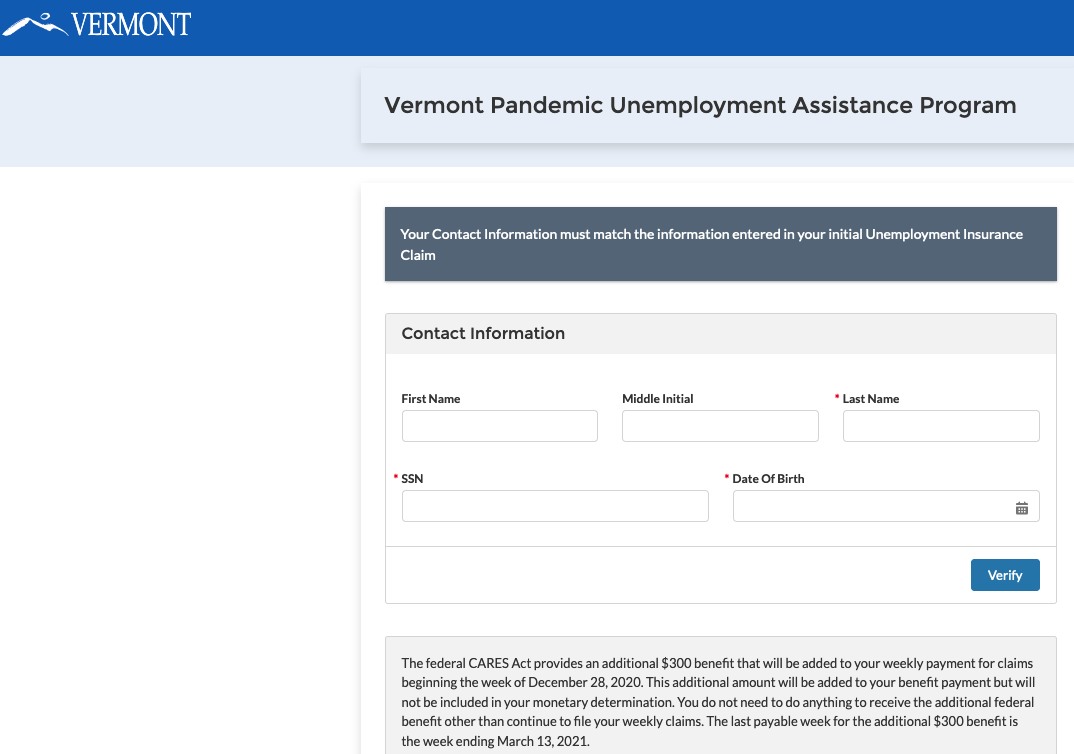
Until being contacted by this reporter on Monday, the state of Vermont had at least five separate Salesforce Community sites that allowed guest access to sensitive data, including a Pandemic Unemployment Assistance program that exposed the applicant’s full name, Social Security number, address, phone number, email, and bank account number.

This misconfigured Salesforce Community site from the state of Vermont was leaking pandemic assistance loan application data, including names, SSNs, email address and bank account information.
Vermont’s Chief Information Security Officer Scott Carbee said his security teams have been conducting a full review of their Salesforce Community sites, and already found one additional Salesforce site operated by the state that was also misconfigured to allow guest access to sensitive information.
“My team is frustrated by the permissive nature of the platform,” Carbee said.
Carbee said the vulnerable sites were all created rapidly in response to the Coronavirus pandemic, and were not subjected to their normal security review process.
“During the pandemic, we were largely standing up tons of applications, and let’s just say a lot of them didn’t have the full benefit of our dev/ops process,” Carbee said. “In our case, we didn’t have any native Salesforce developers when we had to suddenly stand up all these sites.”
Earlier this week, KrebsOnSecurity notified Columbus, Ohio-based Huntington Bank that its recently acquired TCF Bank had a Salesforce Community website that was leaking documents related to commercial loans. The data fields in those loan applications included name, address, full Social Security number, title, federal ID, IP address, average monthly payroll, and loan amount.
Huntington Bank has disabled the leaky TCF Bank Salesforce website. Matthew Jennings, deputy chief information security officer at Huntington, said the company was still investigating how the misconfiguration occurred, how long it lasted, and how many records may have been exposed.
KrebsOnSecurity learned of the leaks from security researcher Charan Akiri, who said he wrote a program that identified hundreds of other organizations running misconfigured Salesforce pages. But Akiri said he’s been wary of probing too far, and has had difficulty getting responses from most of the organizations he has notified to date.
“In January and February 2023, I contacted government organizations and several companies, but I did not receive any response from these organizations,” Akiri said. “To address the issue further, I reached out to several CISOs on LinkedIn and Twitter. As a result, five companies eventually fixed the problem. Unfortunately, I did not receive any responses from government organizations.”
The problem Akiri has been trying to raise awareness about came to the fore in August 2021, when security researcher Aaron Costello published a blog post explaining how misconfigurations in Salesforce Community sites could be exploited to reveal sensitive data (Costello subsequently published a follow-up post detailing how to lock down Salesforce Community sites).
On Monday, KrebsOnSecurity used Akiri’s findings to notify Washington D.C. city administrators that at least five different public DC Health websites were leaking sensitive information. One DC Health Salesforce Community website designed for health professionals seeking to renew licenses with the city leaked documents that included the applicant’s full name, address, Social Security number, date of birth, license number and expiration, and more.
Akiri said he notified the Washington D.C. government in February about his findings, but received no response. Reached by KrebsOnSecurity, interim Chief Information Security Officer Mike Rupert initially said the District had hired a third party to investigate, and that the third party confirmed the District’s IT systems were not vulnerable to data loss from the reported Salesforce configuration issue.
But after being presented with a document including the Social Security number of a health professional in D.C. that was downloaded in real-time from the DC Health public Salesforce website, Rupert acknowledged his team had overlooked some configuration settings.
Washington, D.C. health administrators are still smarting from a data breach earlier this year at the health insurance exchange DC Health Link, which exposed personal information for more than 56,000 users, including many members of Congress.
That data later wound up for sale on a top cybercrime forum. The Associated Press reports that the DC Health Link breach was likewise the result of human error, and said an investigation revealed the cause was a DC Health Link server that was “misconfigured to allow access to the reports on the server without proper authentication.”
Salesforce says the data exposures are not the result of a vulnerability inherent to the Salesforce platform, but they can occur when customers’ access control permissions are misconfigured.
“As previously communicated to all Experience Site and Sites customers, we recommend utilizing the Guest User Access Report Package to assist in reviewing access control permissions for unauthenticated users,” reads a Salesforce advisory from Sept. 2022. “Additionally, we suggest reviewing the following Help article, Best Practices and Considerations When Configuring the Guest User Profile.”
In a written statement, Salesforce said it is actively focused on data security for organizations with guest users, and that it continues to release “robust tools and guidance for our customers,” including:
Control Which Users Experience Cloud Site Users Can See
Best Practices and Considerations When Configuring the Guest User Profile
“We’ve also continued to update our Guest User security policies, beginning with our Spring ‘21 release with more to come in Summer ‘23,” the statement reads. “Lastly, we continue to proactively communicate with customers to help them understand the capabilities available to them, and how they can best secure their instance of Salesforce to meet their security, contractual, and regulatory obligations.”